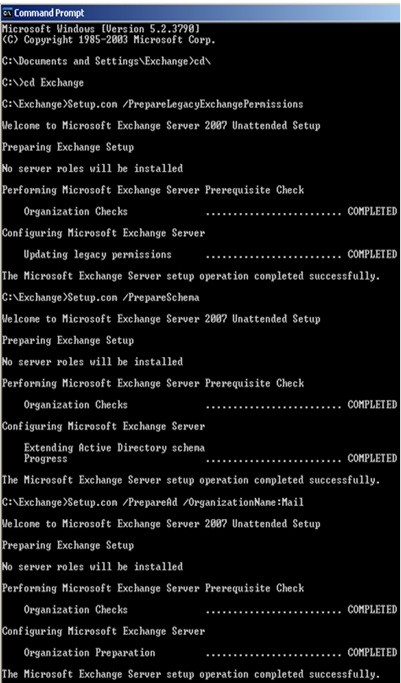
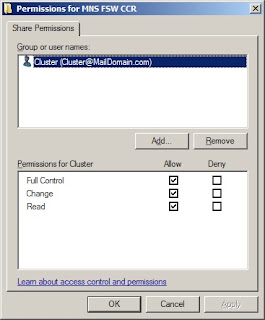
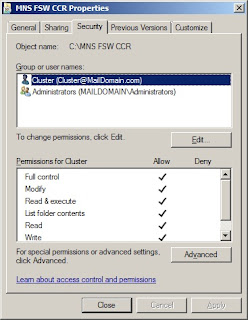
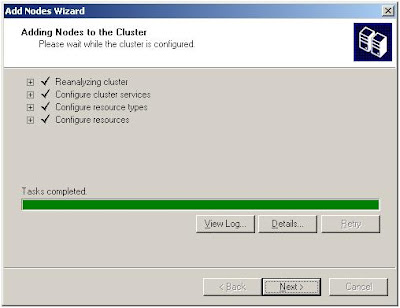
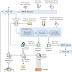
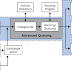
The Exchange 2007 transport pipeline consists of the following components and processes:
SMTP Receive When an Email is received at the Edge Transport server, anti-spam and antivirus agents filter connections and content of the Email and help to identify the sender and the recipient of a Email. Once Email is known as clean with no virus and with a valid sender's domain stamps, Email is allowed to enter the organisation.
When Email is messages are received at a Hub Transport server, transport rules and conditions are checked and applied, if any anti-spam and antivirus agents are configured, these agents provide an additional layer of anti-spam and antivirus protection to the Email.
An Email goes to various events at The SMTP Receive session before it is accepted into the organization. Once Email complete all checks through SMTP Receive and is not rejected by receive events or by an anti-spam and antivirus agent, it is put in the Submission queue.
Submission - Where Submission process takes place, In which Email is submitted into a Submission queue. Then from there the categorizer will pick Emails for categorization.
Categorizer - On the Edge Transport server categorization is a short process in which the message is put directly in the delivery queue and from the delivery queue, the message is routed to a computer that is running a Hub Transport server role in the organization.
On the Hub Transport server, the categorizer completes the actual categorization steps like Recipient resolution, Addressing, Expansion, Bifurcation, Content conversion and mail flow rules that are defined by the receipient organization are applied. After messages have been categorized, they are put into a delivery queue.
Delivery Queue - A mailbox delivery queue delivers the message to a local mailbox by using the Store driver. A remote delivery queue delivers the message to a remote recipient through a Send connector.
Local Delivery - Emails that are sent to a recipient with a mailbox in the same Active Directory site as the Hub Transport server on which categorization is carried out are delivered locally. All Emails delivered locally are picked up from a delivery queue by the Store driver and put in the recipient’s inbox on a Mailbox server.
SMTP Send Emails that are sent to recipients with a mailbox in the Active Directory sites that differs from the Hub Transport server role on which categorization occurred are delivered remotely or outside the organization. All Emails that are sent to a different Active Directory site, to a Send connector of a Hub Transport server that can deliver the message to the intended recipient. All Emails those are required to deliver through the Internet must be routed through a Send connector to an Edge Transport server that can send messages to the Internet for delivery outside the organization.
Client Access and Unified Messaging Scenarios Several client access scenarios and Unified Message scenarios do not interact directly with the transport pipeline. Users of Microsoft Office Outlook 2003, Office Outlook Web Access, Outlook by Phone, and Exchange ActiveSync interact directly with the Client Access server role, Unified Messaging server role, and Mailbox server role to access their mailbox. In each case, when mail is sent, the message is put in the sender’s outbox directly on the Mailbox server by Outlook or the Client Access server on behalf of the sender.
After the message is put in the sender’s outbox, the Store driver is alerted by the Microsoft Exchange Mail Submission service, retrieves the message from the sender’s Outbox, and then puts it into the Submission queue on a Hub Transport server in the same Active Directory site as the mailbox from which the message was retrieved.
Note - Outlook by Phone requires interaction with the Client Access server and with the Mailbox server through the Unified Messaging server.
Also, remember the type of connections which server roles makes with each other while processing certain requests.Its really helpfull while troubleshooting the issue, if we are sure about which type of protocol is used.
SMTP Receive When an Email is received at the Edge Transport server, anti-spam and antivirus agents filter connections and content of the Email and help to identify the sender and the recipient of a Email. Once Email is known as clean with no virus and with a valid sender's domain stamps, Email is allowed to enter the organisation.
When Email is messages are received at a Hub Transport server, transport rules and conditions are checked and applied, if any anti-spam and antivirus agents are configured, these agents provide an additional layer of anti-spam and antivirus protection to the Email.
An Email goes to various events at The SMTP Receive session before it is accepted into the organization. Once Email complete all checks through SMTP Receive and is not rejected by receive events or by an anti-spam and antivirus agent, it is put in the Submission queue.
Submission - Where Submission process takes place, In which Email is submitted into a Submission queue. Then from there the categorizer will pick Emails for categorization.
Categorizer - On the Edge Transport server categorization is a short process in which the message is put directly in the delivery queue and from the delivery queue, the message is routed to a computer that is running a Hub Transport server role in the organization.
On the Hub Transport server, the categorizer completes the actual categorization steps like Recipient resolution, Addressing, Expansion, Bifurcation, Content conversion and mail flow rules that are defined by the receipient organization are applied. After messages have been categorized, they are put into a delivery queue.
Delivery Queue - A mailbox delivery queue delivers the message to a local mailbox by using the Store driver. A remote delivery queue delivers the message to a remote recipient through a Send connector.
Local Delivery - Emails that are sent to a recipient with a mailbox in the same Active Directory site as the Hub Transport server on which categorization is carried out are delivered locally. All Emails delivered locally are picked up from a delivery queue by the Store driver and put in the recipient’s inbox on a Mailbox server.
SMTP Send Emails that are sent to recipients with a mailbox in the Active Directory sites that differs from the Hub Transport server role on which categorization occurred are delivered remotely or outside the organization. All Emails that are sent to a different Active Directory site, to a Send connector of a Hub Transport server that can deliver the message to the intended recipient. All Emails those are required to deliver through the Internet must be routed through a Send connector to an Edge Transport server that can send messages to the Internet for delivery outside the organization.
Client Access and Unified Messaging Scenarios Several client access scenarios and Unified Message scenarios do not interact directly with the transport pipeline. Users of Microsoft Office Outlook 2003, Office Outlook Web Access, Outlook by Phone, and Exchange ActiveSync interact directly with the Client Access server role, Unified Messaging server role, and Mailbox server role to access their mailbox. In each case, when mail is sent, the message is put in the sender’s outbox directly on the Mailbox server by Outlook or the Client Access server on behalf of the sender.
After the message is put in the sender’s outbox, the Store driver is alerted by the Microsoft Exchange Mail Submission service, retrieves the message from the sender’s Outbox, and then puts it into the Submission queue on a Hub Transport server in the same Active Directory site as the mailbox from which the message was retrieved.
Note - Outlook by Phone requires interaction with the Client Access server and with the Mailbox server through the Unified Messaging server.
Also, remember the type of connections which server roles makes with each other while processing certain requests.Its really helpfull while troubleshooting the issue, if we are sure about which type of protocol is used.